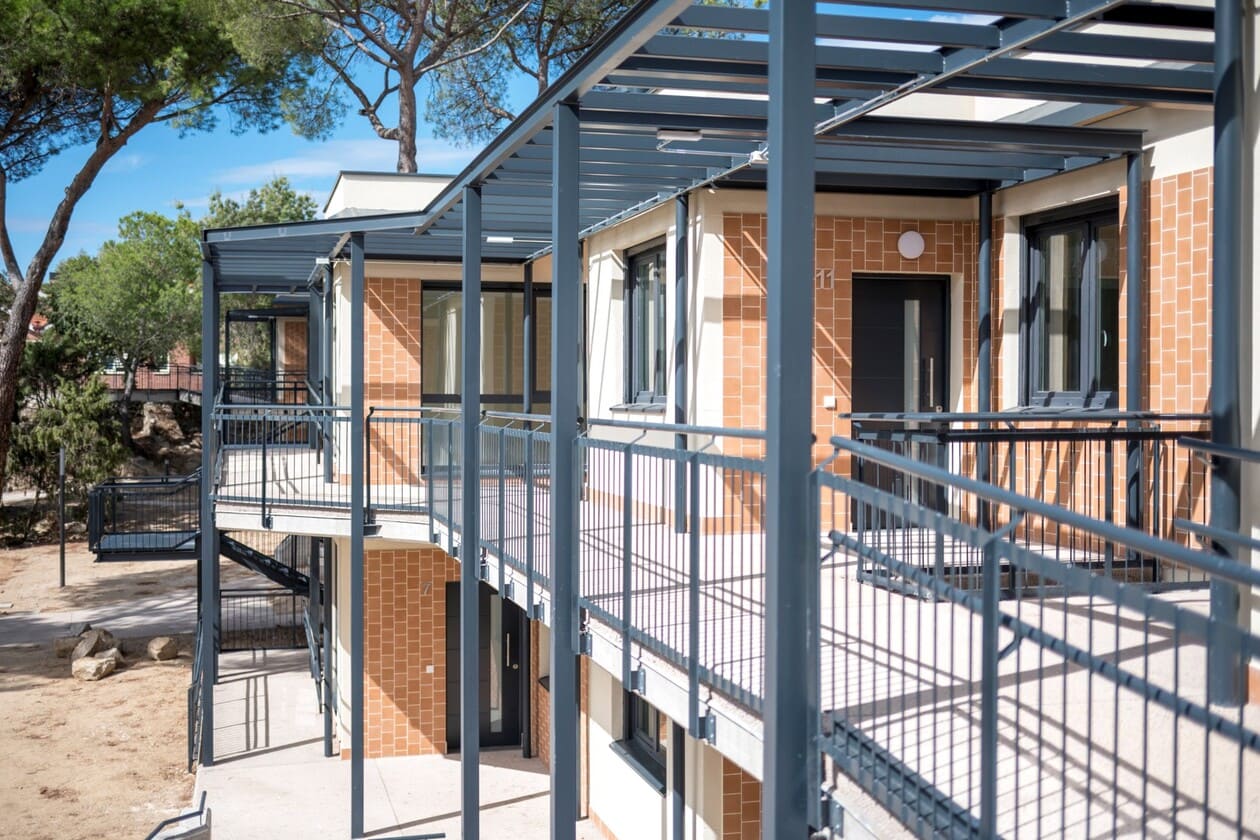
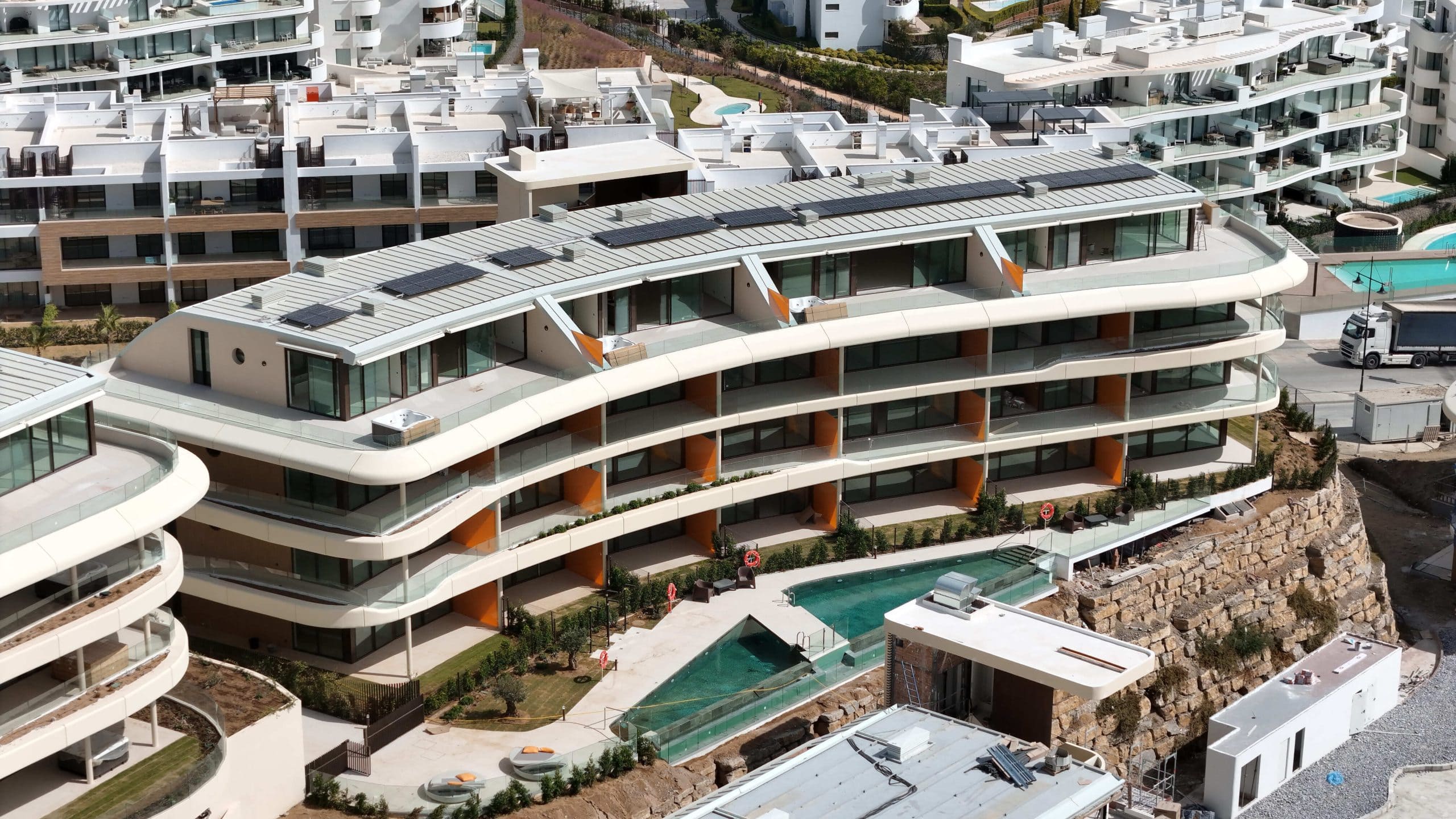
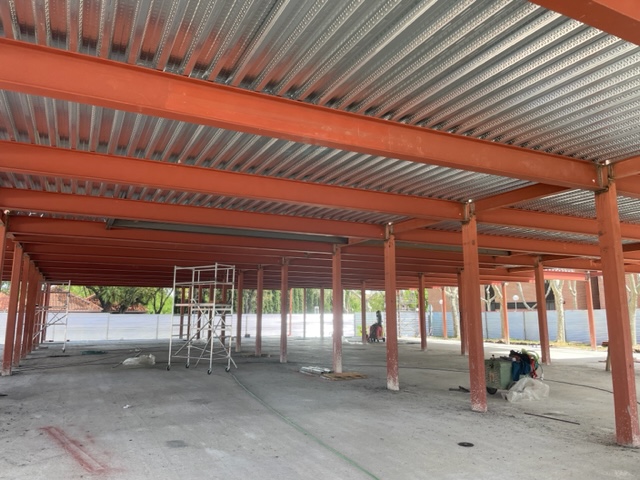
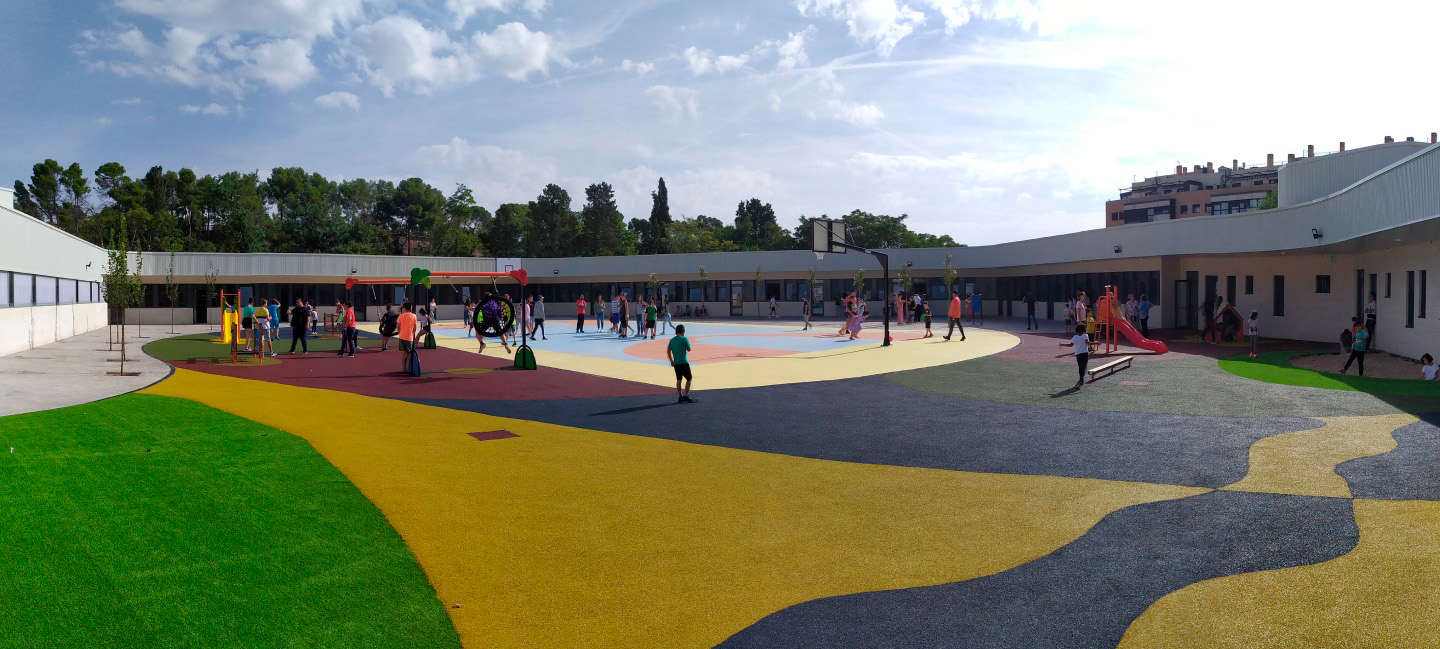
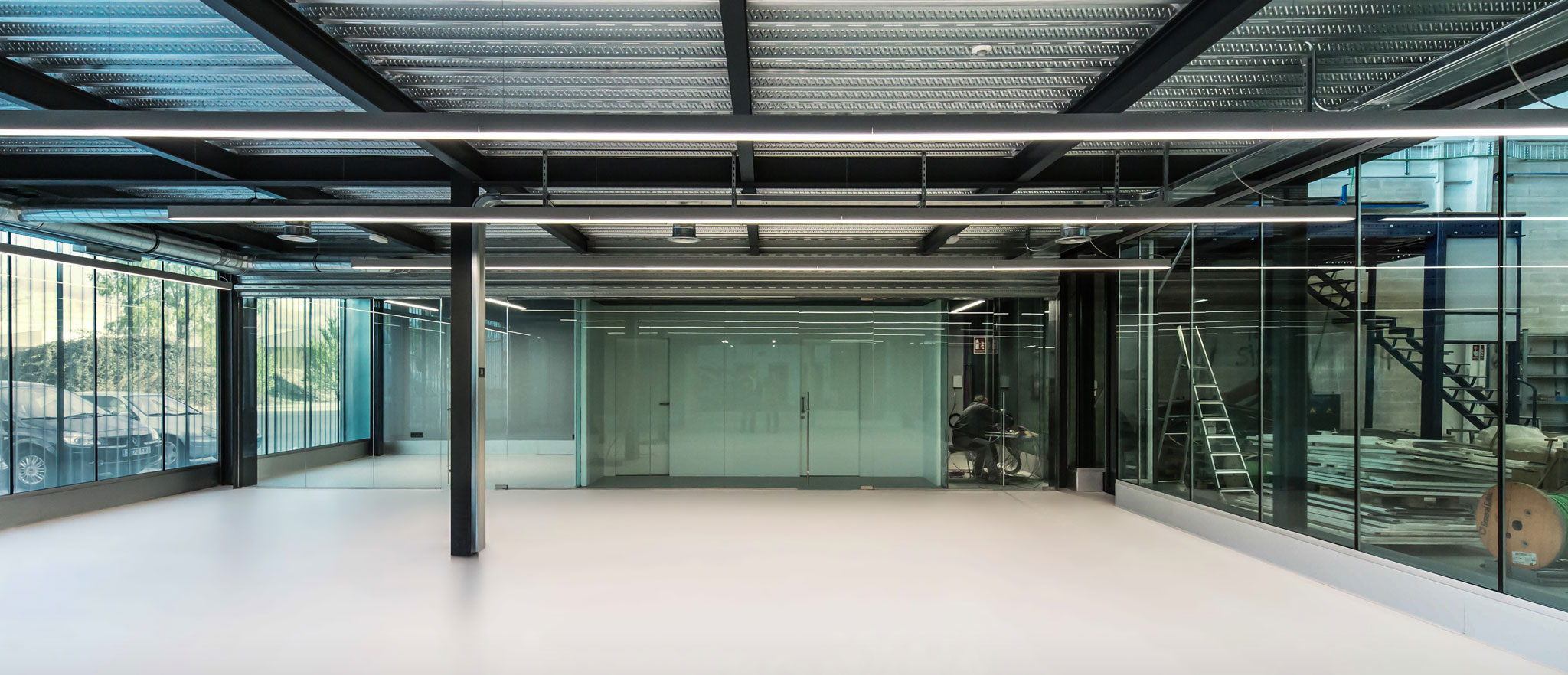
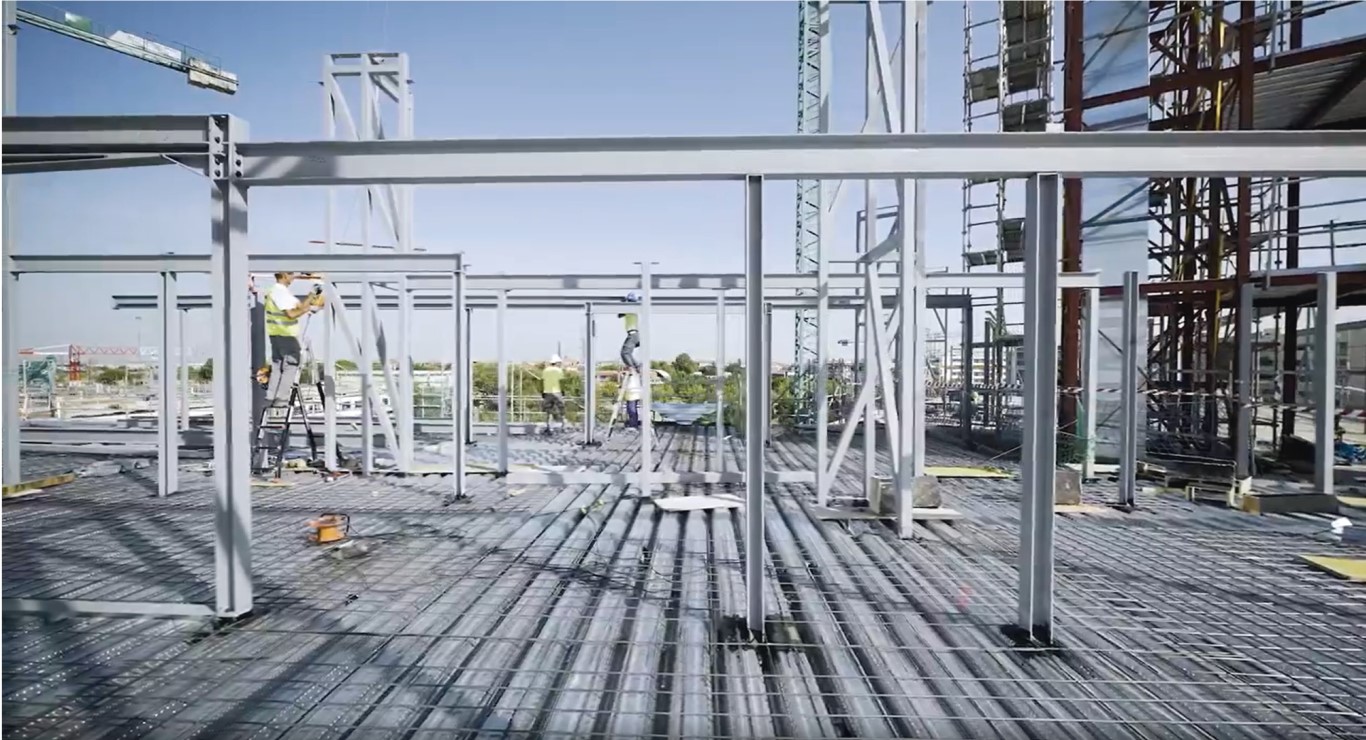
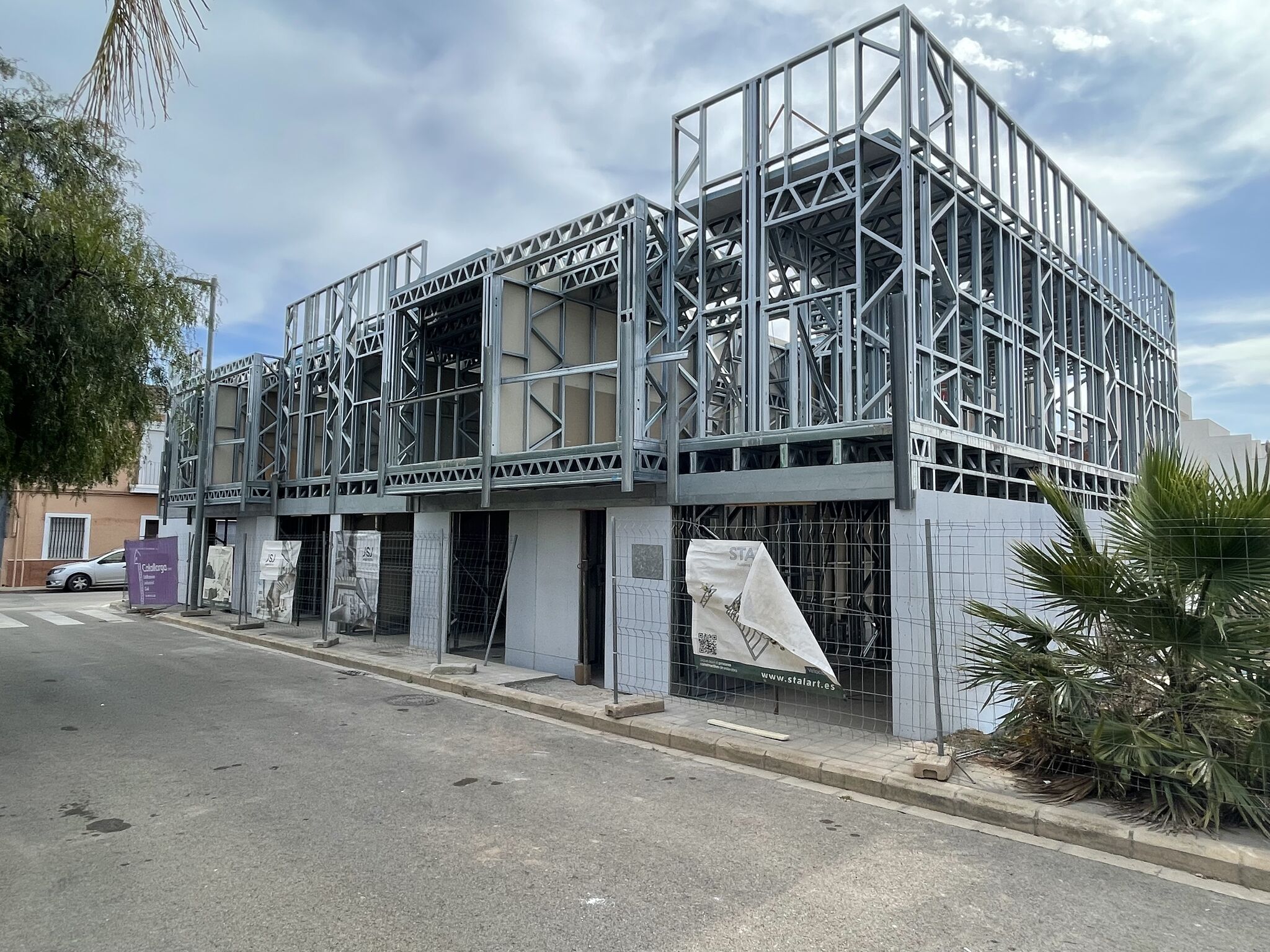
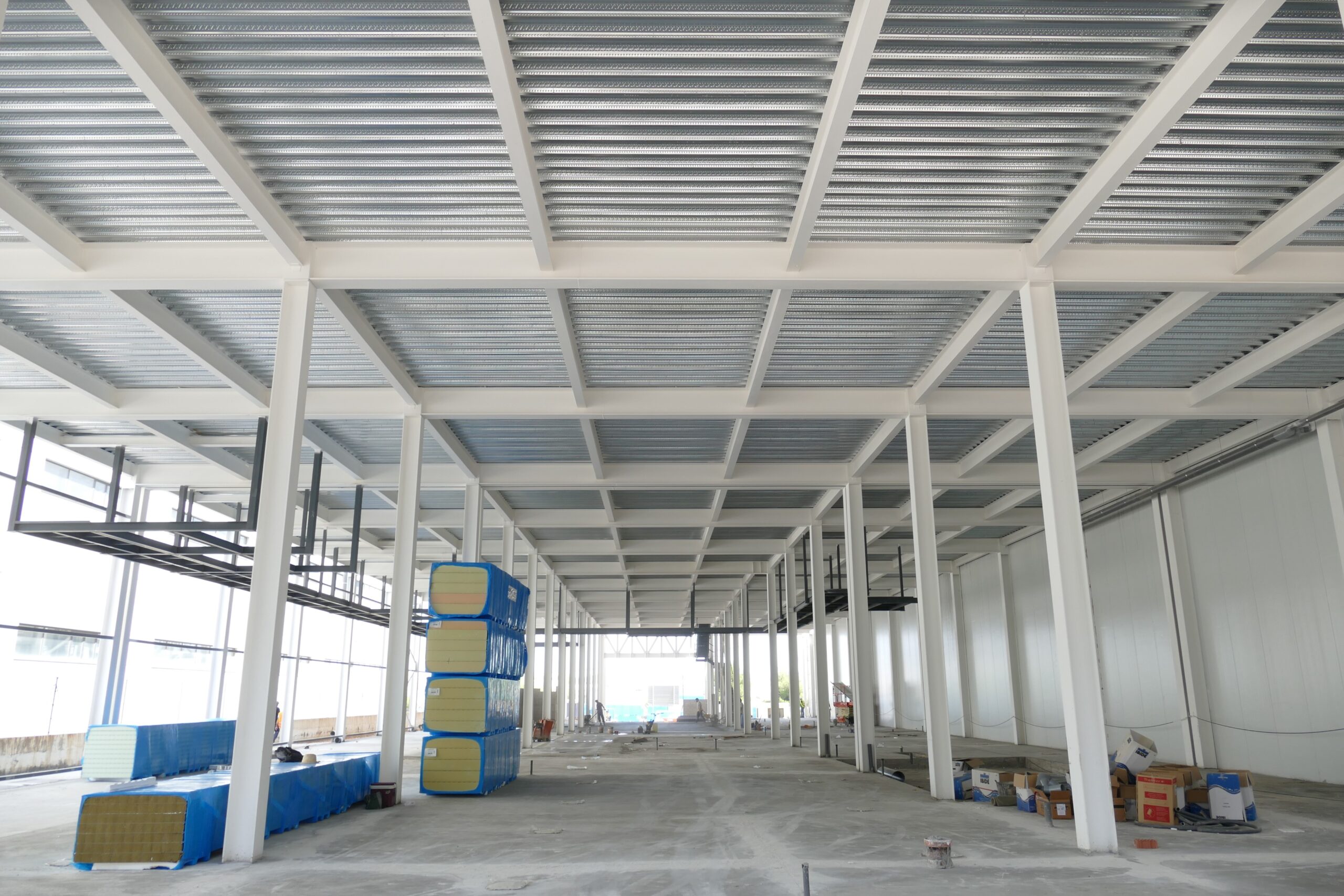
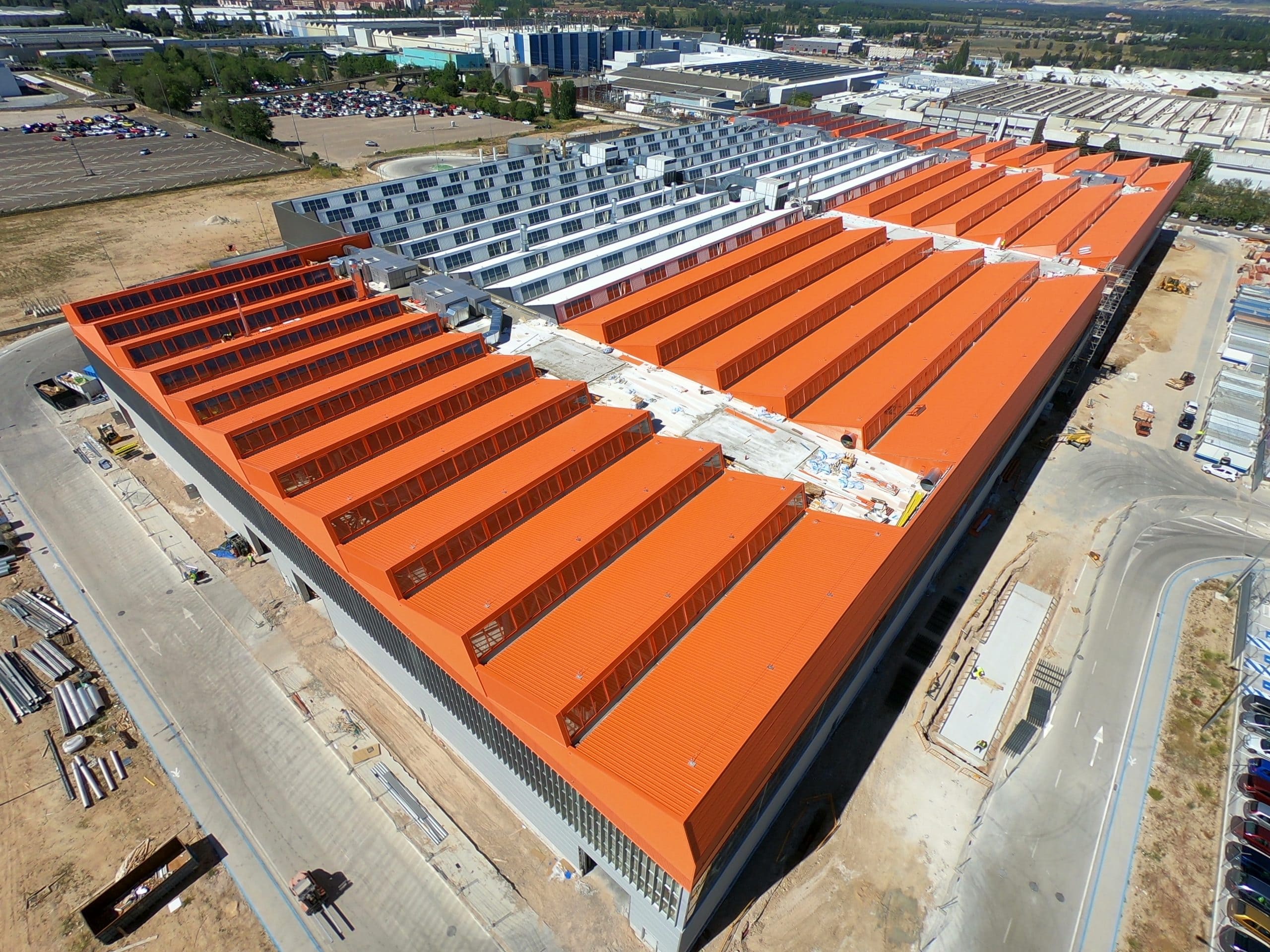
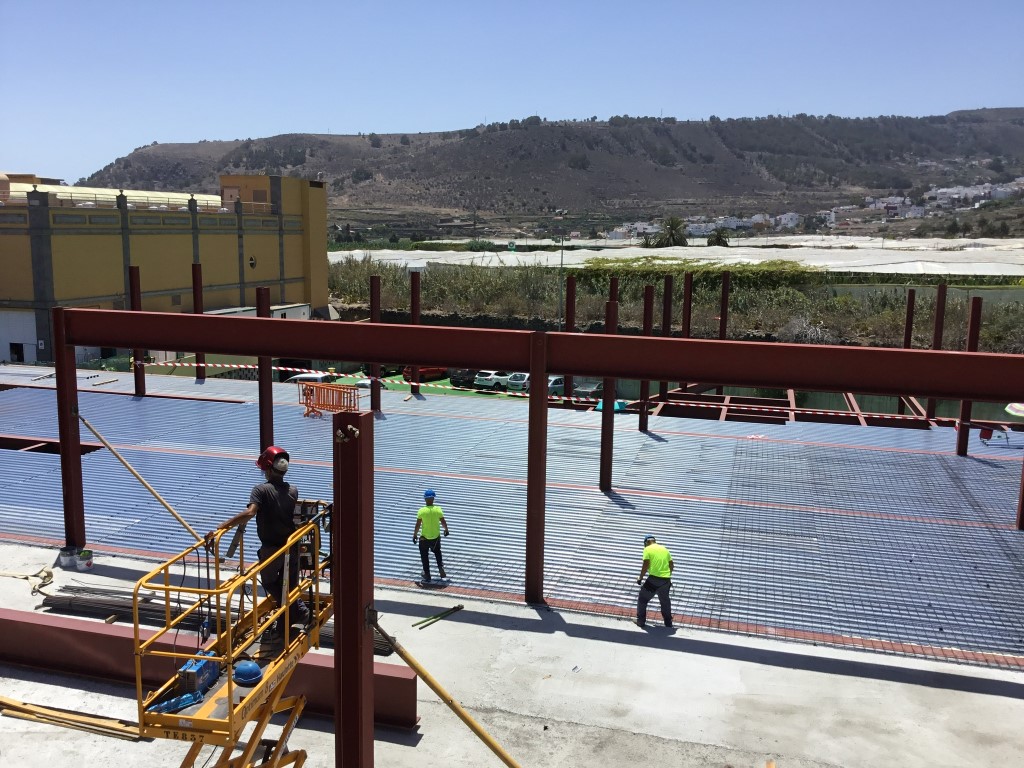
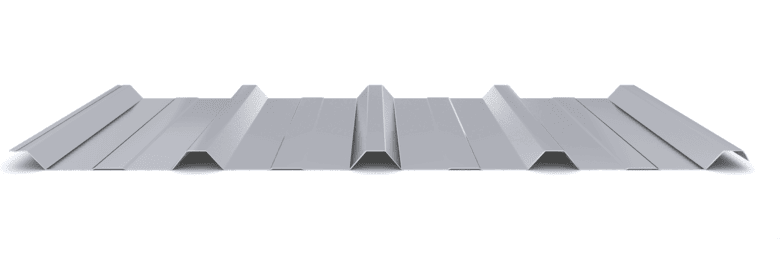
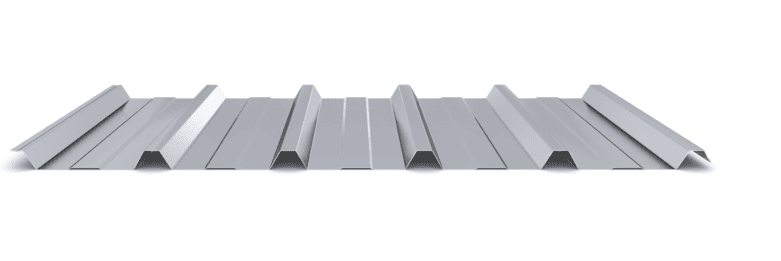
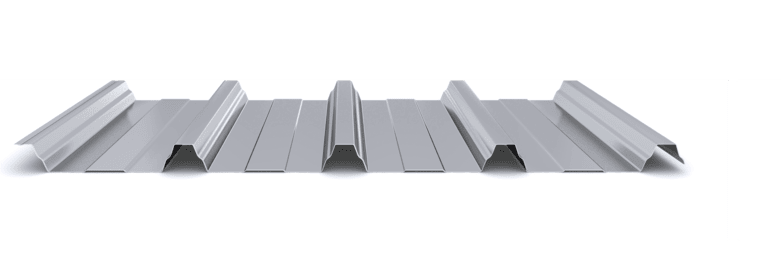
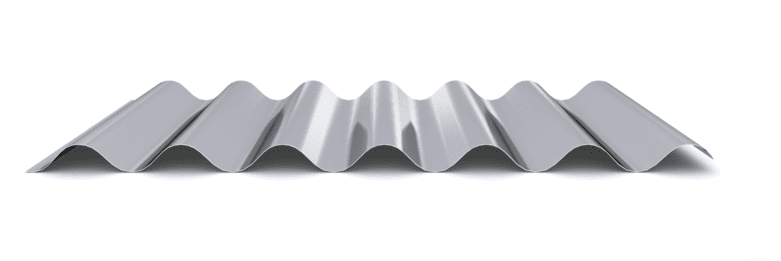
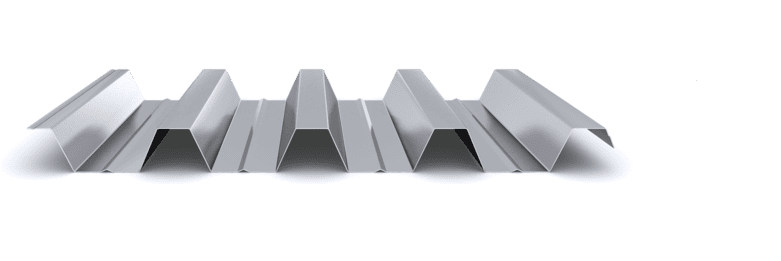
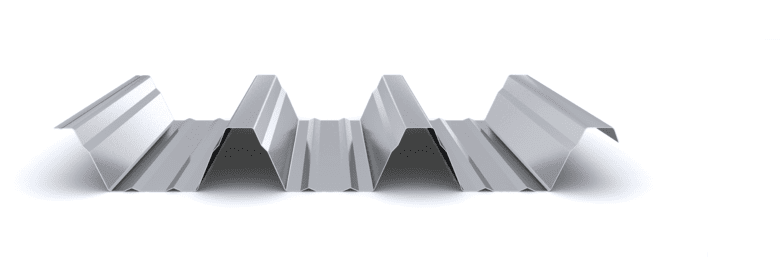
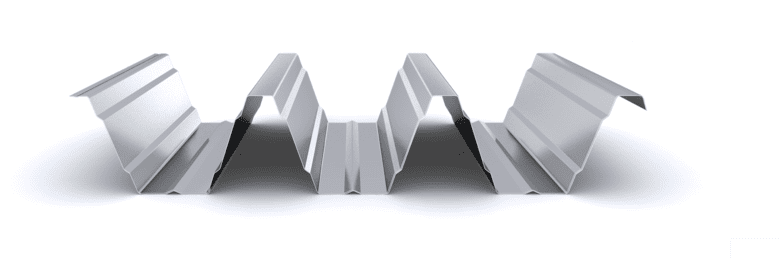
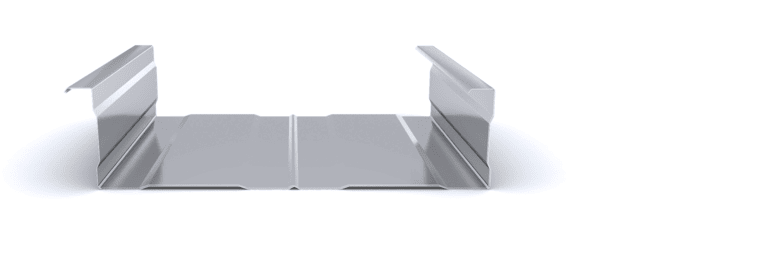
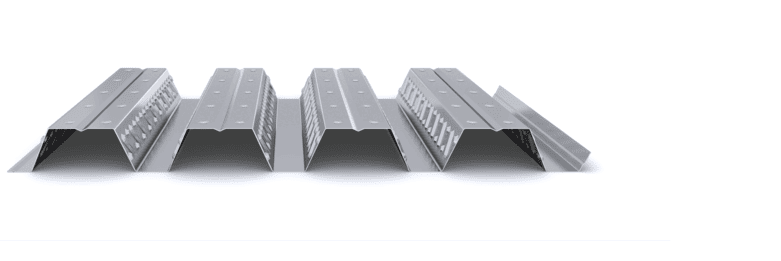
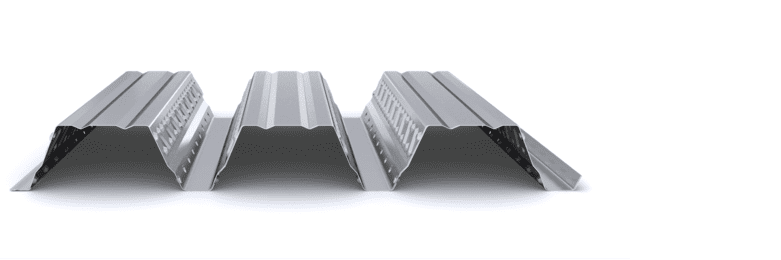
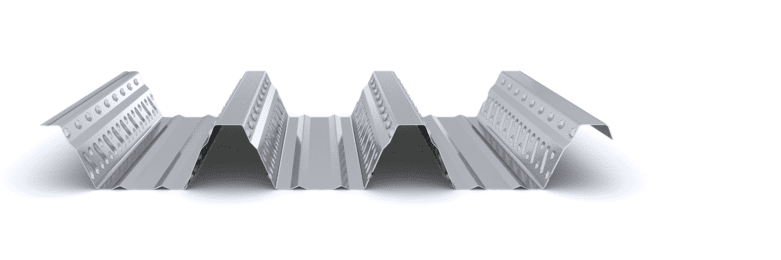
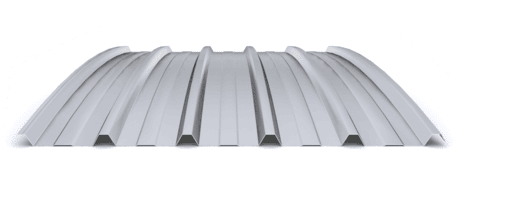
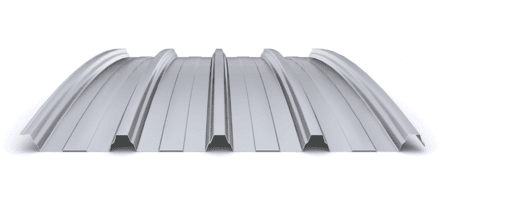
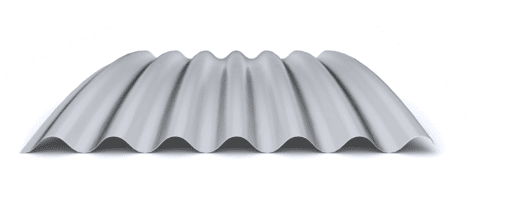
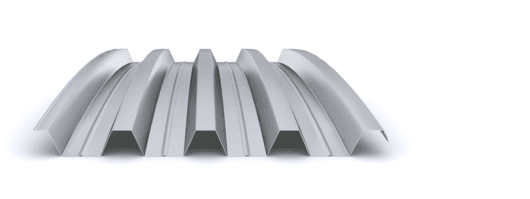
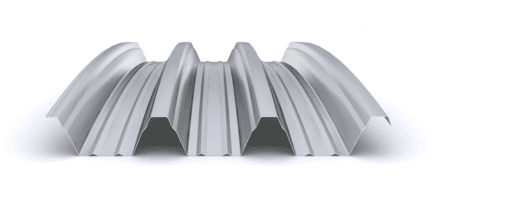
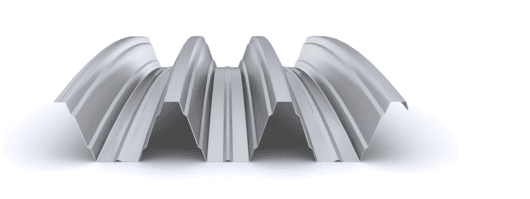
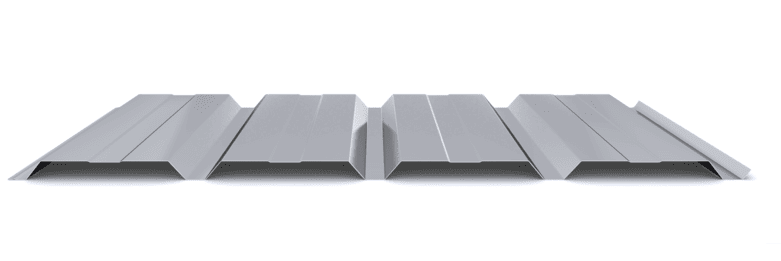
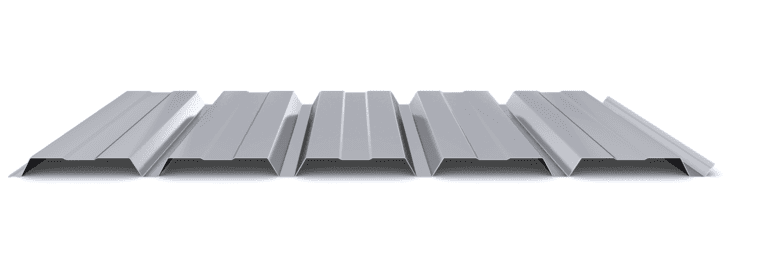
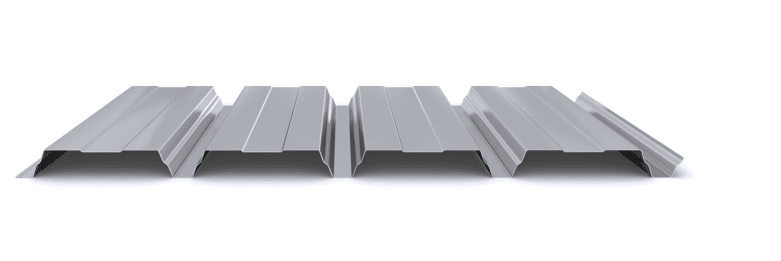
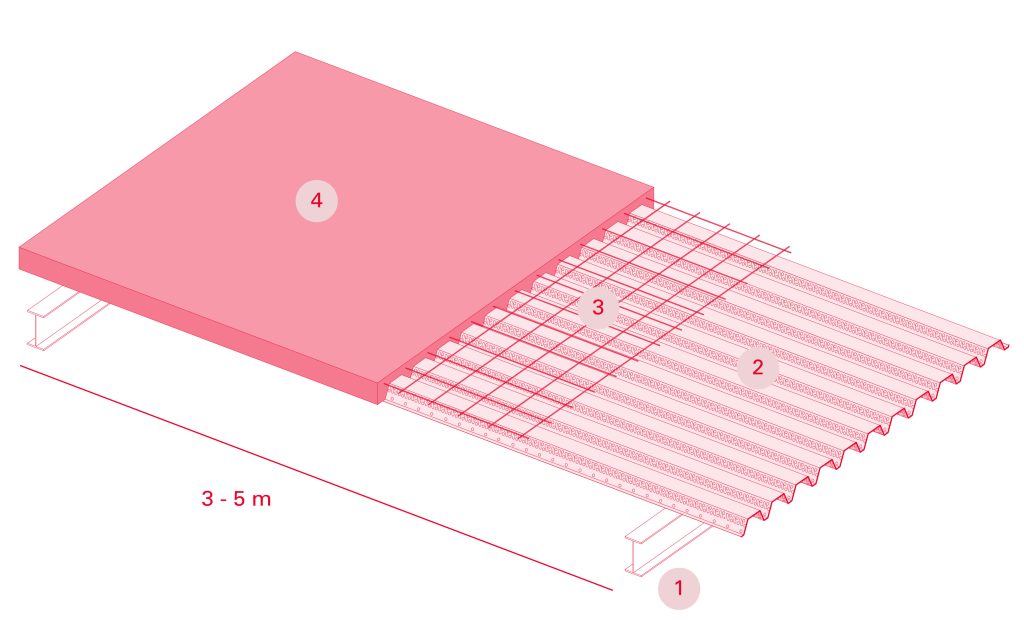
The composite slab system is made up of a galvanized metal composite floor deck that serves as formwork for a concrete slab executed in situ. Once the concrete has reached the characteristic strength of the project, the ribbed profile and the concrete slab work together.
During the formwork phase, the profile supports the loads of execution and pouring of the concrete. In the mixed phase, the profile collaborates with the concrete through specific embossing, acting as positive reinforcement and forming a mixed cross section. It is for this reason that the composite floor deck is also known as a composite or mixed slab.
Using this solution, light slabs can be made, with a self-weight of less than 2 kN/m², through an agile and simple execution procedure, especially in those slabs that do not require shoring. In those cases in which shoring is not an impediment, greater separations between the support beams of the slab can be achieved.
The main advantages of composite slabs are:
- Versatility: Adapts to any type of plant, offering flexibility in architectural design.
- Strength/Weight Ratio: Provides greater resistance with a lower own weight, which allows reducing the overall weight of the structure. This is possible thanks to a minimum slab depth of 120 mm.
- Speed of installation: The elimination of shoring allows the concreting of more than one floor simultaneously, considerably reducing the execution time.
- Cost Reduction: A reduction in labor costs is achieved by avoiding shoring and in materials, by using a smaller volume of concrete. This implies a reduction in the weight of the structure and waste.
In addition to the main advantages, the composite slab offers additional benefits, such as the simplicity of the construction process, the ease of assembly and cleaning on site, its function as formwork providing a safe platform to work on, and its contribution to structural bracing, thus improving its functionality and efficiency in construction.